Welding laser trabem
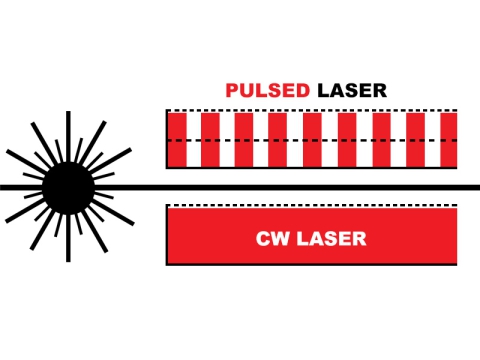
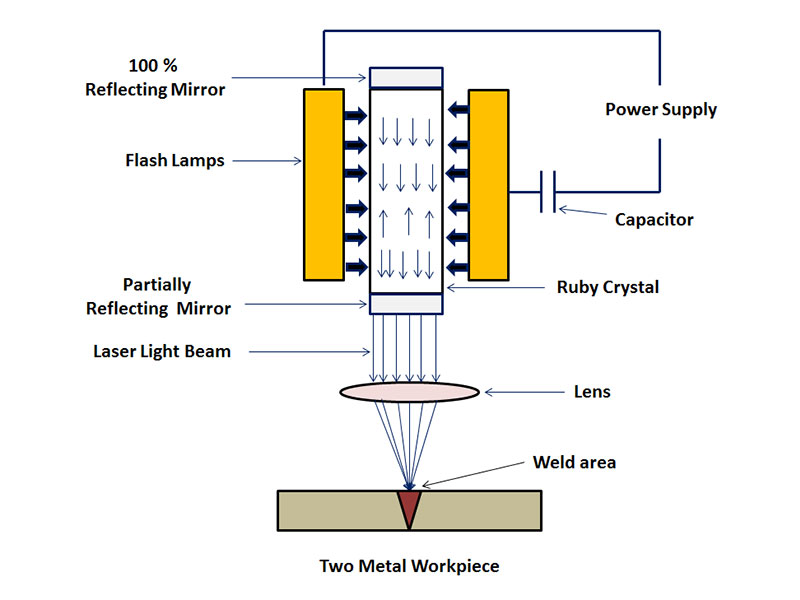
Radius laser glutino summus efficacia est et methodus valde accurata glutino utens summus energiae densitatis trabes laseris tamquam fons caloris eius. Welding fieri potest a radiis laseris continui seu pulsu. Secundum principia laser welding, processus ulterius in duo dividi possunt: conductio caloris glutino et laser glutino profundo. Potentia densitatis infra 104 ~ 105 W/cm2 refertur ad calefactionem conductionis glutino. In illo tempore penetratio profunditatis est tenui cursu lento glutino; cum potentia densitatis major est quam 105~107W /cm2, sub actione caloris, superficies metallica recipit recessum in "foraminis" apparentiam ad formam penetrationis altae glutino.
Features
Features of Fast welding Speed and large aspect Ratio
Laser glutino plerumque utitur radiis laser continuis ad connexionem materiae perficiendam. Processus physicus metallurgicus simillimus est trabi glutino electronico, id est, vis conversionis mechanismi per structuram clavem "clavis" perficiendam.
Sub alta potentia densitatis laser irradiatio, materia evaporat et format parva foramina. Hoc foramen parvum vapore repletum est instar corporis nigri, omnem fere vim trabes incidentis absorbentis. Aequilibrium temperatura in cavitate circiter 2500C est. A calore parietis exterioris transfertur cavitas caliditatis, liquefaciens metallo cavum ambiente. Parva foramina repleta sunt vapore calidissimus generatus ex continua evapora- tione parietis materiae sub radio lucis.
4 Parietes e parvis foraminibus fusili metallo circumdant et liquido metallo materiam solidam cingit. (In frequentissimis glutino processibus et laseris conductionis glutino vis est 1. of fluere.
Hoc est, parvum foramen ac metallum fusile circa foramen progredietur antrorsum velocitate trabes ducens. Metallum fusile per foramen parvum foramen relictum implet, et postea condensat, et globus formatur. Omnes processus superiores tam celeriter fiunt ut celeritas glutino plura metra per minutias facile attingere possit.
1. Laser tignum glutino est fusio weldiana, qua laser trabes utitur ut fons industriae, et iuncta iuncta impacta est.
2. Trabs laseris per plana elementum opticum (ut in speculo) dirigi potest, et deinde trabs in commissurae pugillo commissurae cum reflexione posito vel lens elemento projicitur.
3. Laser tignis welding is not-contact welding. Nulla pressura in operatione requiritur, sed iners gas opus est ad oxidationem lacus fusilis prohibendam. In consectetur interdum interdum elit.
4. Laser glutino coniungi potest cum MIG glutino ad formam laser MIG composito glutino ad magnam penetrationem glutino perficiendam, dum calor initus valde deminutus ad MIG glutino comparatus est.
Applications
Machina glutinatio laser late in tam alta praecisione agrorum fabricandorum ut autocineta, naves, aeroplana, et celeritate plenas blasphemiae adhibetur. Valde emendavit qualitatem vitae pro hominibus ac etiam industriae instrumentum ad praecisionem machinalis propulsavit.
Arcus Plasma Welding
Plasma arcus glutino significat modum fusionis glutini qui utitur plasma arcus summus energia densitatis trabes sicut principium caloris glutino. In glutino gas ion (arcum ion formans) et gas protegens (ad tuendum stagnum liquefactum et commissurae glutino ab effectibus aeris nocivis) puri argon sunt. Electrodes in plasmate arcui glutino adhibiti plerumque electrodes tungsten et interdum metallico (filum glutino) repleri debent. Generaliter, in DC iunctio affirmativa methodus adoptatur (tungsten virga cum electrode negativo iungitur). Ergo plasma arcus glutino est essentialiter glutino gas- clypeo glutino cum effectu compressionis.
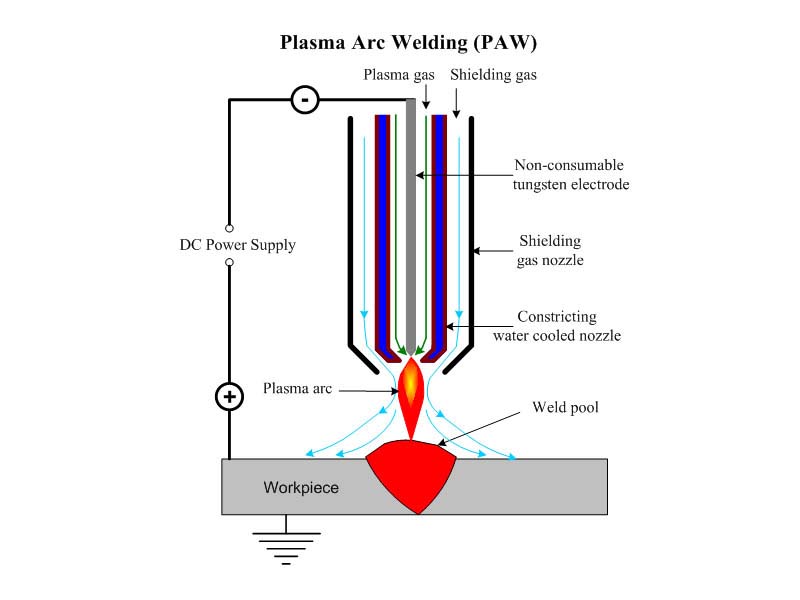
Plasma arcus glutino proprietates energiae energiae, productivitatis altae, celeritas glutino celeritas, parva vis deformatio, et solitudo electrica stabilis habet, et ad tenuissimas laminas et cistae materias glutino apta est. Praecipue apta est variis refractoribus, facile oxidizatis, materiae metallica-sensitivae (ut tungsten, molybdenum, cuprum, nickel, titanium, etc.).
Gas calefactio arcus dissociatur et comprimitur, cum per alvum aquarum refrigeratum in celeritate alta transiens, vim densitatis et gradum dissociationis augens, arcum plasma formans. Eius stabilitas, calorificus valor et temperatus sunt altiores arcu generali, unde maiorem vim habet et celeritas glutino. Gas arcum plasma formans et gasum circumfusum scutulatum vulgo argon puro utuntur. Prout materiae proprietates variarum officinarum, utuntur nonnulli helium, nitrogenium, argonis, vel mixturam utriusque.
Features
1. Micro-trabs plasma arcus glutino rudiculas et laminas tenues conglutinare potest.
2. Cum parvo foramine effectus, melius percipere potest conglutinationem simplicem et duplex postesque formationem liberam.
3. Arcus plasma habet densitatem energiam altam, columnam arcus altam caliditatem, et facultatem penetrationis validam. Potest consequi 10-12mm denso ferro sine revellere coneris. Duplex formans in uno tempore conflari potest. Celeritas glutino celeritas est, productio alta est, et vis parva deformatio est.
4. Apparatus relative complicatus est, consumptio gasorum magna est, coetus stricte requisita in alvi et munditia fabricae habet, et solum ad glutino umbraticis idoneus est.
Applications
Plasma glutino maximi momenti est in productione industriae, praesertim ad mixturam aeris et aeris, titanium et titanium stannum, stannum chalybem, ferrum immaculatum, molybdenum et alia metalla aerospace, quae adhibentur in militaribus et aliis industriis incisis, qualia sunt quaedam species missilis missilis in vasis tenuibus mixturae et vasis emissilibus fabricandis.
Sumptus, sustentationem et efficientiam operational
Aliquot factores comparando electiones technologiarum inter trabem laseris glutino et plasma arcui glutino ad applicationes industriales includunt sumptus, sustentationem et efficientiam operationalem.
Pretium Analysis
Trabes glutino laserae collocationem initialem altam requirit cum apparatum complicatum comparatur ad plasma arcui glutino. Valet generalis industriae systemata laser welding plerumque sursum tendit $200,000, cum plasma arcus systemata glutino alicubi in amplitudine constat $1ut 0,000 $50,000. Nihilominus, LBW potentiam habet ad significantes diuturnum tempus peculi sumptus gratiarum ad augendas rates processus necnon minimas post-coniugationes necessarias. Plasma glutino altiores sumptus consumabiles habere potuit ad operationem continuam.
victum Requirements
Quia partes consumabiles, ut electrodes et nozzales gasi, crebrius fatigant, plasma arcus systematis glutino frequentiorem sustentationem requirere solet. Contra, systemata laser glutino consumables pauciores requirunt, sed earum perspectiva et laser fontes interdum purgatione et recalibratione indigent. Cum recte servetur, fontes laser perdurare potest plusquam 20,000 horarum minore tempore. Systemata plasma, quamvis simpliciora, frequentiores interpellationes cum consumables gerunt possunt experiri.
operational efficientia
Artificia laseris glutino sunt multo velociores et accuratiores, velocitates attingentes tam altae quam 10 metra per minutas in tenuissimas materias, unde valde specimen productionis massae. Etiam zonas caloris affectatas minutissimas producit, proindeque materiam minimam distorquens, sic productum qualitatem augens. Plasma glutino in crassioribus materiis efficax est, quamquam tardius cursu, saepe etiam egens superaddita manu ad purgandum welds, sicut stridor.
Dum laser conglutinatio requirit altiorem obsidionem gratuita upfront, eius efficacia et rarior necessitas ad sustentationem saepe gratuita beneficia in longo spatio praebent, praesertim applicationes ad altam praecisionem requirentes. Plasma arcus glutino est adhuc bonum opus minus implicatum et operationes minores.